ARM

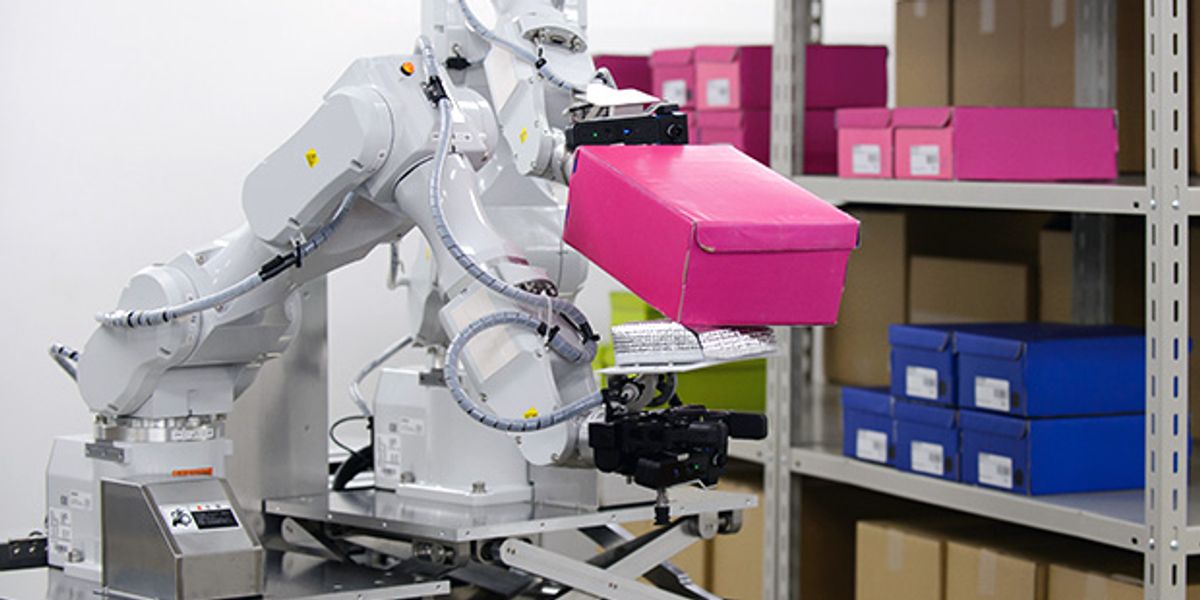
ARM is a two-armed robot designed to perform complex manipulation tasks. It was created for DARPA's Autonomous Robotic Manipulation program. Its official name is ARM, but you can call him Robbie.
- Creators
- Year
- 2010
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
When RE2, the firm hired to build the ARM robot, asked DARPA for guidance about the robot's appearance, DARPA said the robot should look like a Star Wars character.

History
Led by Dr. Gill Pratt, DARPA's Autonomous Robotic Manipulation (ARM) program aimed at developing hardware and software to significantly advance robots' ability to manipulate and interact with the physical world. The ARM robot was built as a test bed for the research and development of algorithms to perform human-level tasks quickly and with minimal direction. In 2010, six institutions were selected for the first phase of the program, with each group receiving a one-armed robot to work with. In late 2011, DARPA evaluated each group's performance and subsequently initiated the program's second phase, where focus turned to complex bimanual manipulation scenarios. The program also included an outreach component, whose aim is to show the robotics community and the public how the technologies developed might be used in the future and to get people excited about robotics and engineering in general.


Specs
- Overview
Bimanual manipulation, autonomous and teleoperation modes, designed with commercially available parts, simulation package.
- Status
Inactive
- Year
2010
- Website
- Width
- 274 cm
- Height
- 198 cm
- Weight
- 204 kg
- Sensors
Stereo camera, high-resolution camera, LIDAR, stereo microphones, position sensors (in the joints), force-torque sensor (end-effector), and tactile sensors (fingers and palm).
- Actuators
Cable-driven Barrett WAM Arm and Barrett Hand.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 26 (Neck: 4 DoF; Arm: 7 DoF x 2; Hand: 4 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Mostly aluminum for WAM arms and sensors; steel for torso and support structure.
- Compute
PC/104 stack for on-board, low-level control of WAM. Sensor processing, path planning, and all high-level functionality performed off-board on dual quad-core Intel Xeon computer.
- Software
Linux on PC/104 and off-board computer. Robot Operating System (ROS) used as main software platform.
- Power
Tethered
- Cost
- $500,000 (estimate)