Ekso

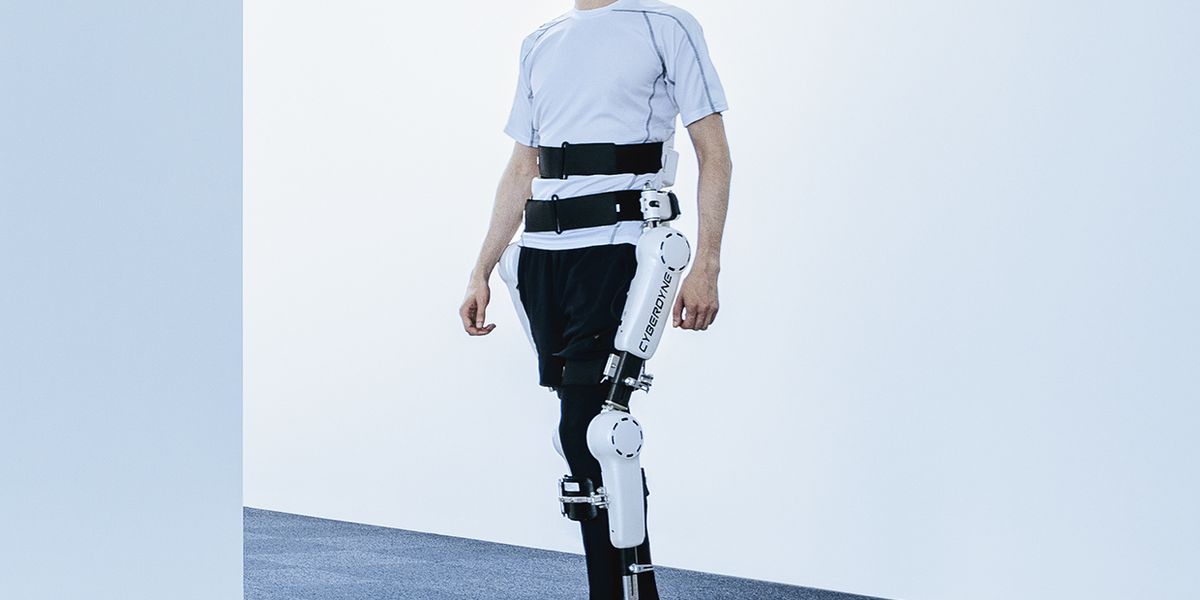
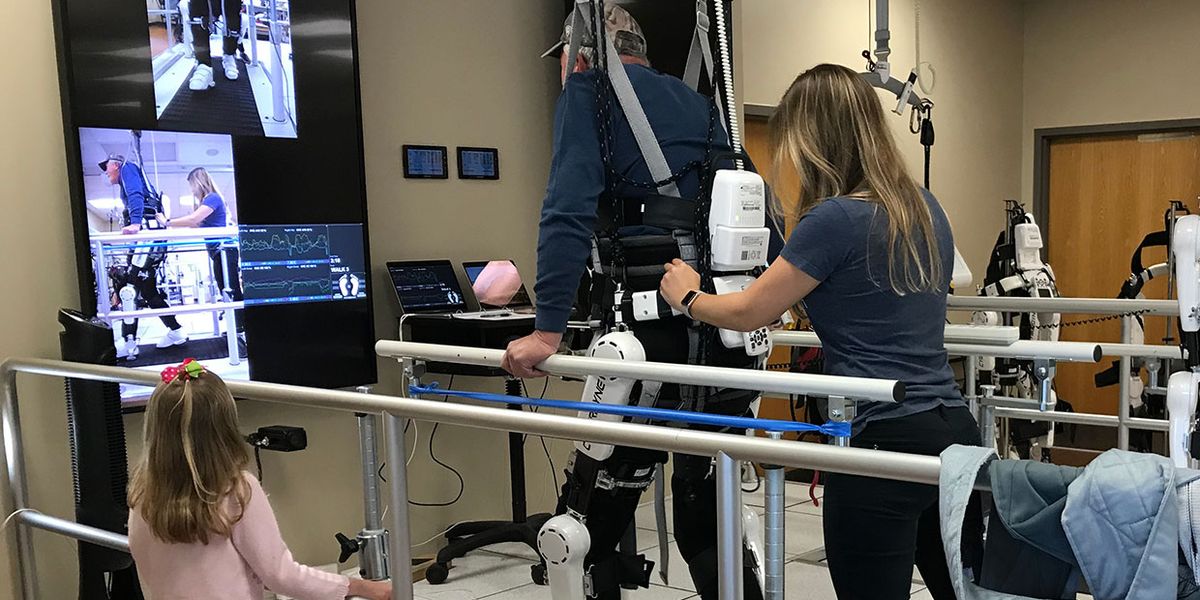
Ekso is a wearable exoskeleton that can augment a person's physical capabilities. It's currently used to get people with lower-extremity paralysis or weakness standing up and walking.
- Creator
- Year
- 2010
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
The exoskeleton transfers its load directly to the ground so the user doesn't bear the weight of the device.


History
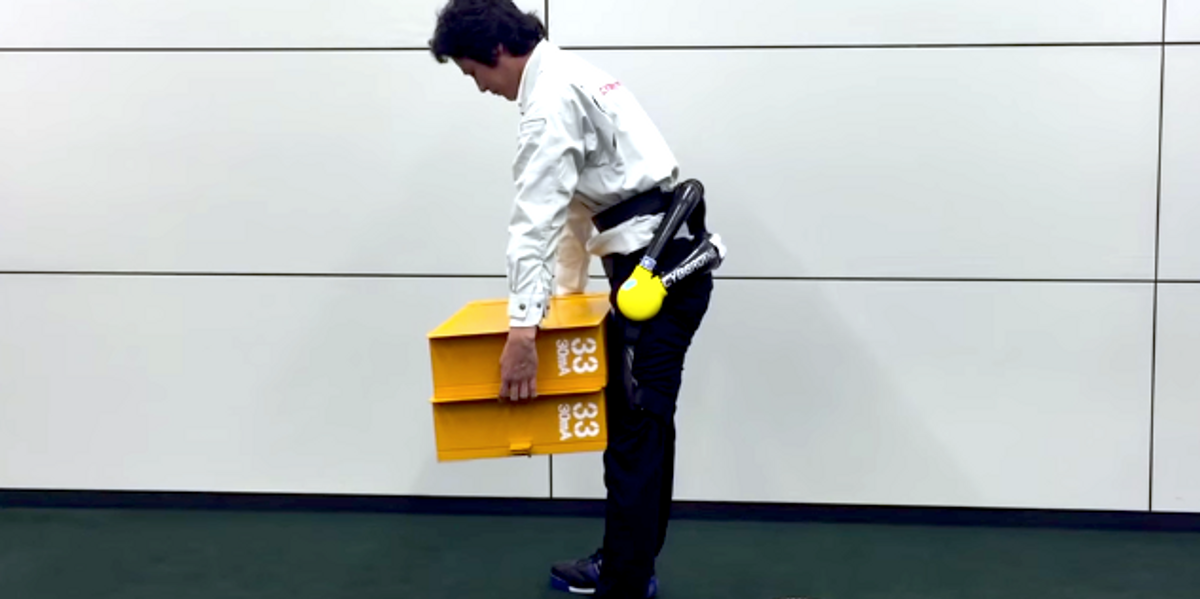
Originally Berkeley Bionics, Ekso Bionics began its evolution in 2005 with the ExoHiker, an exoskeleton that let able-bodied people carry 90 kg (about 200 lb) with minimal exertion. The technology was based on research developed at the University of California, Berkeley. In 2009, the company licensed its load-carrying Human Universal Load Carrier (HULC) system to Lockheed Martin for military development. In 2011, Ekso began testing a new version of its robotic suit in rehabilitation clinics in the United States and Europe. Ekso is now in use at 14 rehabilitation centers around the world. After more trials in clinics and hospitals, the company plans to introduce a model for at-home physical therapy, as well as an upper-body device to help workers with carrying and lifting tasks.


More Images

Specs
- Overview
Capable of adjusting to different body sizes. Equipped with a wireless usage monitor and three walking modes for progressive rehabilitation activity.
- Status
Ongoing
- Year
2010
- Website
- Width
- 54.6 cm
- Height
- 167.6 cm (max); 145 cm | 57 in (min)
- Length
- 35.6 cm
- Weight
- 22.7 kg
- Speed
- 1.61 km/h (depends on user)
- Sensors
More than 30 sensors to measure position, force, and other variables.
- Actuators
Four electromechanical actuators (located at the knees and hips)
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 6 (4 actuated, 2 passive)
- Materials
Advanced aluminum and composite structure.
- Compute
On-board DSP
- Software
Custom C code
- Power
Swappable lithium-polymer batteries
- Cost
- $130,000 (includes Ekso plus support and training program)