Paro

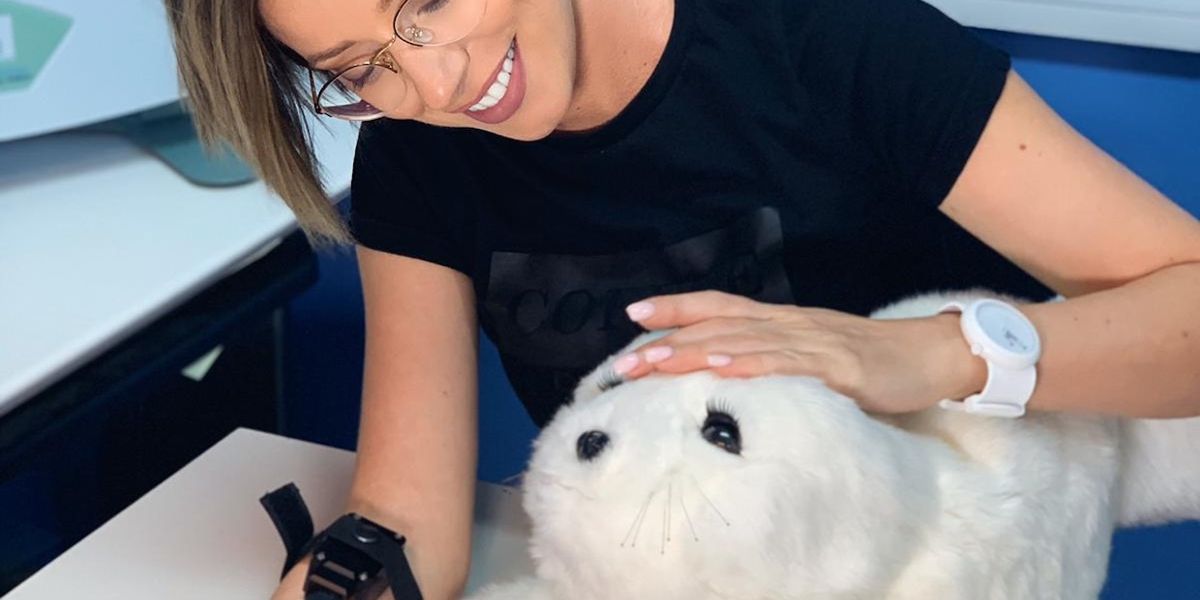
Paro is a robotic baby harp seal designed as a therapeutic tool for use in hospitals and nursing homes. The robot is programmed to cry for attention and respond to its name. It includes an off switch.
- Creator
- Year
- 2004
- Country
- Japan 🇯🇵
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Paro's pacifier doubles as its charger.

History
Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) started the Paro project in 1993. Led by researcher Takanori Shibata, the project unveiled a first-generation robot in 1998. In the years that followed, several new models were developed. In 2004, the eighth generation of the Paro series was developed, and in the following year the robot was commercialized in Japan. In 2009, Paro was introduced in Europe and the United States, where the Food and Drug Administration certified the robot as a "biofeedback medical device." Paro has been used in hospitals and care facilities as a therapeutic tool in about 30 countries.

Specs
- Overview
Voice sampled from real baby harp seals. Covered with white antibacterial fur. Equipped with an internal heating system that keeps its body warm.
- Status
Ongoing
- Year
2004
- Website
- Width
- 35 cm
- Height
- 16 cm
- Length
- 57 cm
- Weight
- 2.7 kg
- Sensors
Light sensor, temperature sensor, tactile sensors (body and whiskers), microphone array.
- Actuators
Seven motors
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 7 (Neck: 2 DoF; Flipper: 1 DoF x 2; Tail: 1 DoF; Eyelid: 1 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Plastic skeleton and body covered with soft white fur.
- Compute
Two 32-bit RISC processors
- Software
Custom software
- Power
Nickel-metal hydride battery, 1.5 hour of operation
- Cost
- $6,000