Salto-1P

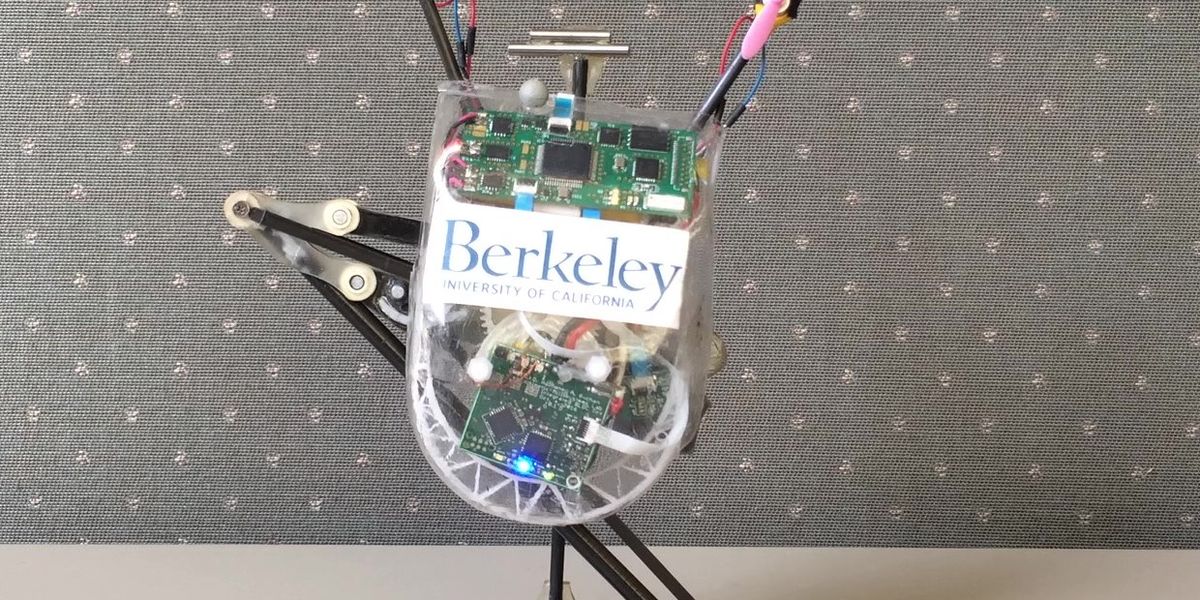
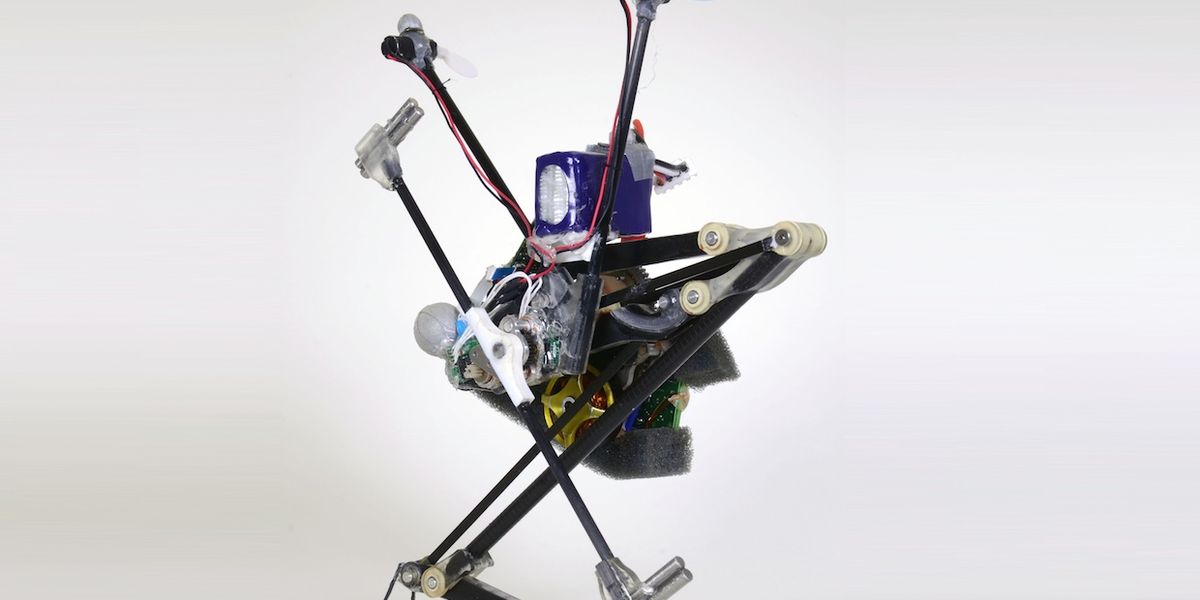
Salto-1P is a small, one-legged jumping robot inspired by the lesser bushbaby, a small nocturnal primate (scientific name Galago senegalensis). Salto-1P's powerful, springy leg enables it to jump high and fast. Using a reaction wheel tail on its side and propeller thrusters on top, it can balance and hop around.
- Creators
University of California at Berkeley and Biomimetic Millisystems Lab
- Year
- 2016
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Salto-1P can measure the force on its leg by measuring the deflection of its spring.

History
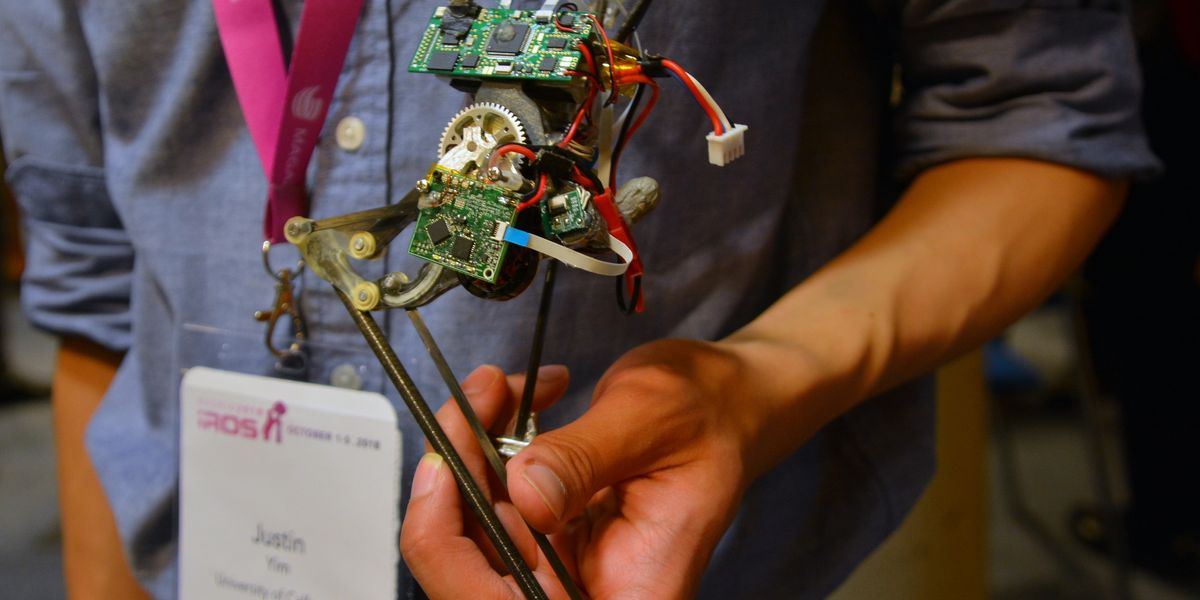
Salto, a small monopedal jumping robot, was created by Justin Yim while he was a PhD student at UC Berkeley in Ron Fearing's Biomimetic Millisystems Lab. Salto-1P uses a small motor and a system of linkages and gears to jump. Because it spends so little time in contact with the ground, the robot needs to do most of its control in the air. To do that, it uses a rotating inertial tail and two little thrusters to stabilize and reorient itself in between jumps. The robot can bounce up and over obstacles, and it can also land on a target spot. Yim is now at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in the Mechanical Science and Engineering department.
Specs
- Overview
Able to perform wall jumps: After jumping off of the ground, Salto-1P can jump off of a wall to get higher. Vertical jumping agility: 1.83 m/s. Maximum jump height 1.25 meters (from crouch to apex).
- Status
Ongoing
- Year
2016
- Website
- Width
- 7 cm
- Height
- 31 cm
- Length
- 13 cm
- Weight
- 0.118 kg
- Speed
- 12 km/h
- Sensors
One TDK InvenSense MPU6000 IMU,
two AMS AS5048B magnetic encoders: one for the extension of the leg and one for the rotation of the tail,
one AMS AS5047P magnetic encoder for the leg brushless motor commutation.- Actuators
One modified Scorpion S-1804-1650KV brushless DC motor with a series-elastic torsional latex spring powers the leg. Two 6-mm diameter brushed motors for the thrusters. Two 6-mm diameter brushed motors in parallel for the tail.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 4 DoF (Leg: 1 DoF, Tail: 1 DoF, Thrusters: 2 DoF)
- Materials
Carbon fiber honeycomb sandwich panel, carbon fiber rods and tubes, cast polyurethane, aluminum gears and gearboxes, aluminum pins, plastic bushings, 3D-printed parts, superglue, hot melt adhesive.
- Compute
ImageProc 2.5 main board based on a dsPIC33FJ128MC706A microcontroller.
Custom brushless DC motor driver board.- Software
Onboard embedded C++. Ground station computer runs ROS or Python.
- Power
14.8-V, 220-mAh lithium-ion battery pack assembled from Tattu 220-mAh 3.7-V 45C cells; around 12 minutes of operation.
- Cost
- A few hundred to a couple thousand U.S. dollars