Raven II

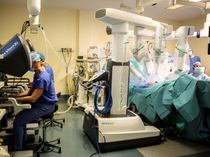
Raven II is a surgical robot designed as an open platform for collaborative research. The goal is to improve telesurgery capabilities as well as enable robots to perform some tasks autonomously.
- Creators
- Year
- 2012
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Its creators named the robot Raven because it is black and comes from the Pacific Northwest. They say there was an acronym at one point, but they've forgotten it.

History
The initial components of the Raven platform were developed in 2005 as part of a DARPA project on the future of battlefield medicine. Raven was designed as a mobile laparoscopic surgical system by a team of researchers led by Blake Hannaford, a professor of robotics at the University of Washington, in Seattle. The idea was making Raven as modular as possible, so it would be more portable than large surgical robots used in hospitals and could be reassembled by a small team of people. The Raven II was developed as a National Science Foundation project on collaborative research to advance surgical robotics. Seven Universities used the Raven II platform, including Harvard University; Johns Hopkins University; University of Nebraska; University of California, Santa Cruz; University of California, Berkeley; and University of Washington. These labs investigated diverse problems involving surgical robots and related technologies and shared their experiences and breakthroughs using Raven as a common platform. Telesurgery experiments with the Raven have involved a remote surgeon operating the robot in the field, under extreme conditions, like underwater in a submarine pod or in high desert temperatures.

Specs
- Overview
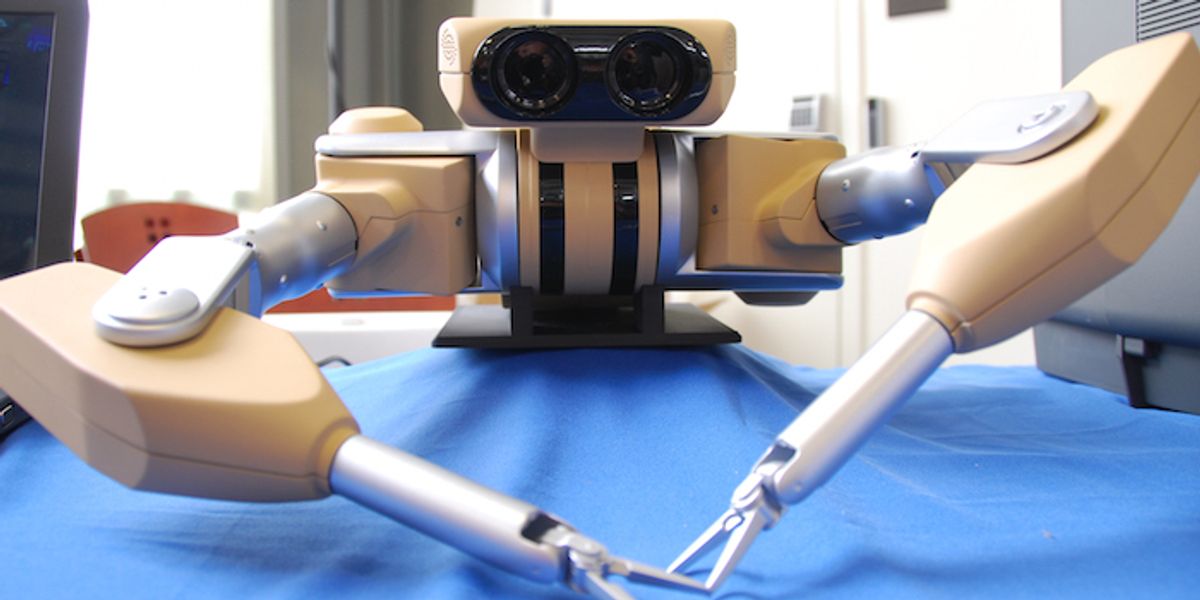
Equipped with two arms and one camera. Surgeon side equipped with Phantom Omni haptic devices. Local control or telesurgery mode via Internet.
- Status
Unknown
- Year
2012
- Website
- Width
- 112 cm
- Height
- 58 cm
- Length
- 127 cm
- Weight
- 46 kg
- Sensors
Each motor with optical encoder to detect shaft rotation and estimate robot joint position. Surgeon side includes user interface and two Phantom Omni haptic devices to detect the surgeon's hand motion.
- Actuators
Each arm has 7 brushless DC motors at base; robot links and tools driven through cable mechanism.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 14 (Arm: 7 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Aluminum and steel cables.
- Compute
Intel Atom-based computer
- Software
Open-source custom software, with ROS, C, and C++ interfaces running on real-time Ubuntu OS. Surgeon interface runs on Windows or other OS.
- Power
Standard 110-V power supply and two 9-V batteries.
- Cost
- $250,000