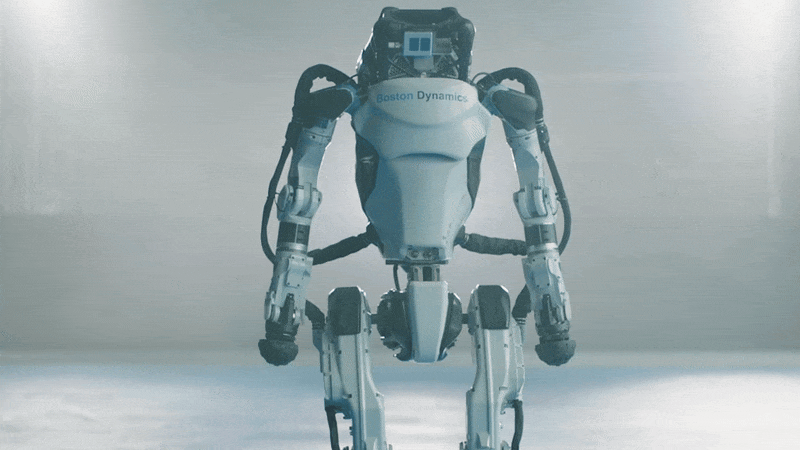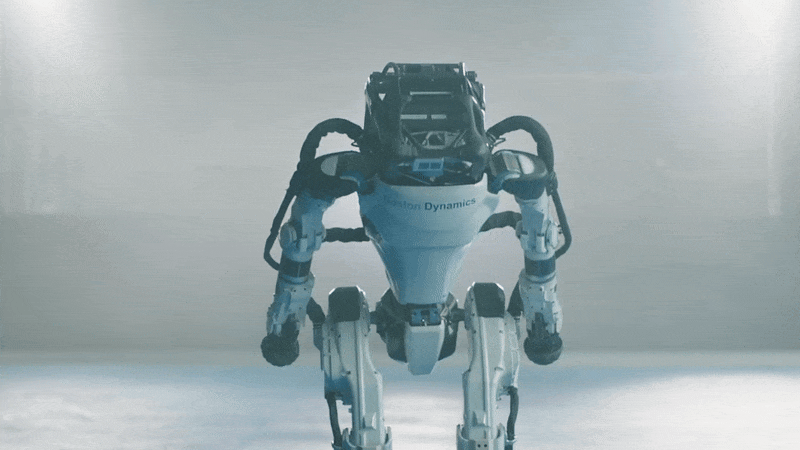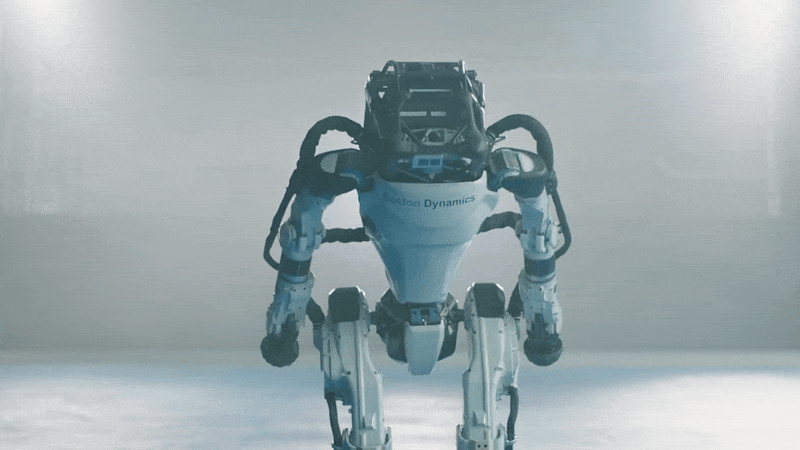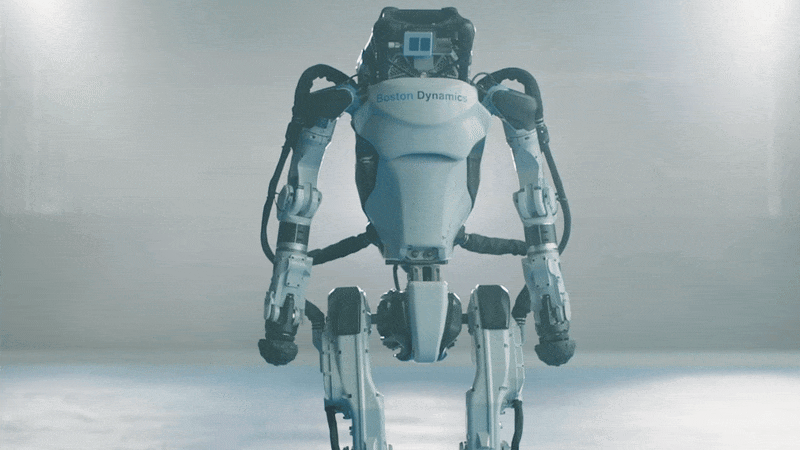
Kojiro

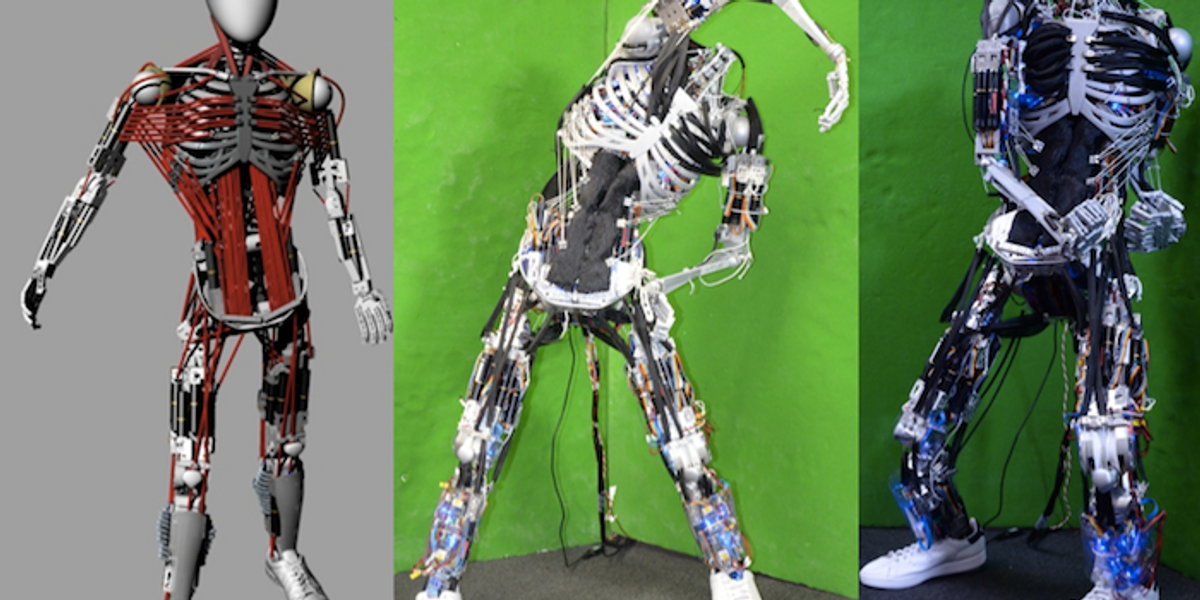
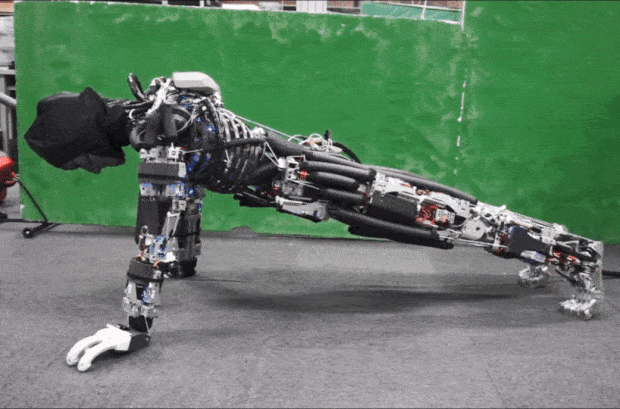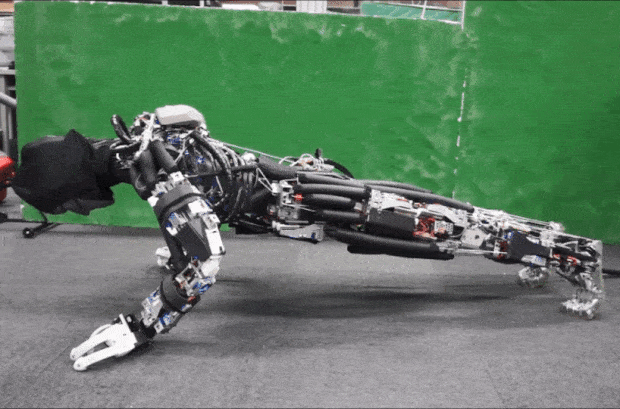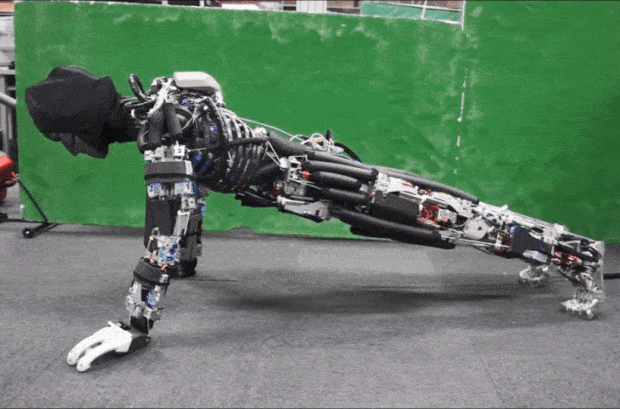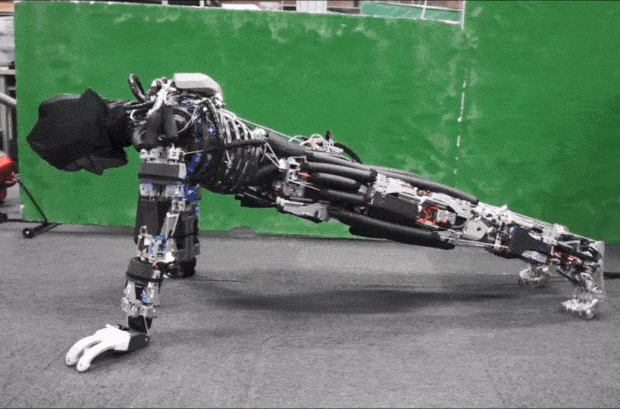
Kojiro is a humanoid with a musculoskeletal system that mimics how the human body works to generate motion. The goal is to build a robot that is light and agile, capable of moving much as people do.
- Creator
- Year
- 2007
- Country
- Japan 🇯🇵
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
In one experiment, researchers programmed Kojiro to hula hoop, but the robot managed only two full revolutions.


History
Kojiro was developed at the University of Tokyo's JSK lab, led by Professor Masayuki Inaba, in the late 2000s. One of the robot's main designers was Yuto Nakanishi, a researcher at the laboratory. Kojiro was designed to mimic the way our skeleton, muscles, and tendons work to generate motion.


More Images

Specs
- Overview
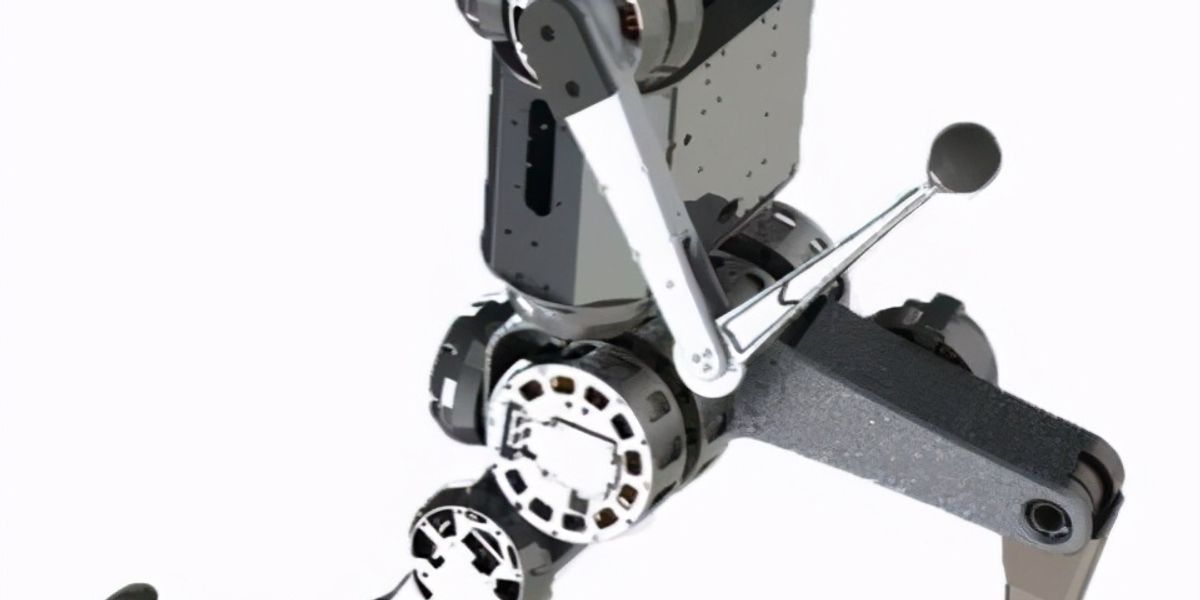
Flexible spine, cable-driven actuation system
- Status
Inactive
- Year
2007
- Website
- Height
- 133 cm
- Weight
- 45 kg
- Sensors
Gyroscope, three-axis accelerometer, six-axis force sensors (in the ankles). Each actuator with rotary encoder, tension sensor, and current and temperature sensors.
- Actuators
Three 1.5-W DC motors, 20 4.5-W DC motors, and 76 40-W DC motors. Motors connected to cables to form artificial muscles.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 56 (Spine: 12 DoF; Head: 3 DoF; Neck: 9 DoF; Leg: 8 DoF x 2; Arm: 5 DoF x 2; Hand: 3 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Tendons made of synthetic fibers, including Vectran, Dyneema, and Zylon.