Asimo

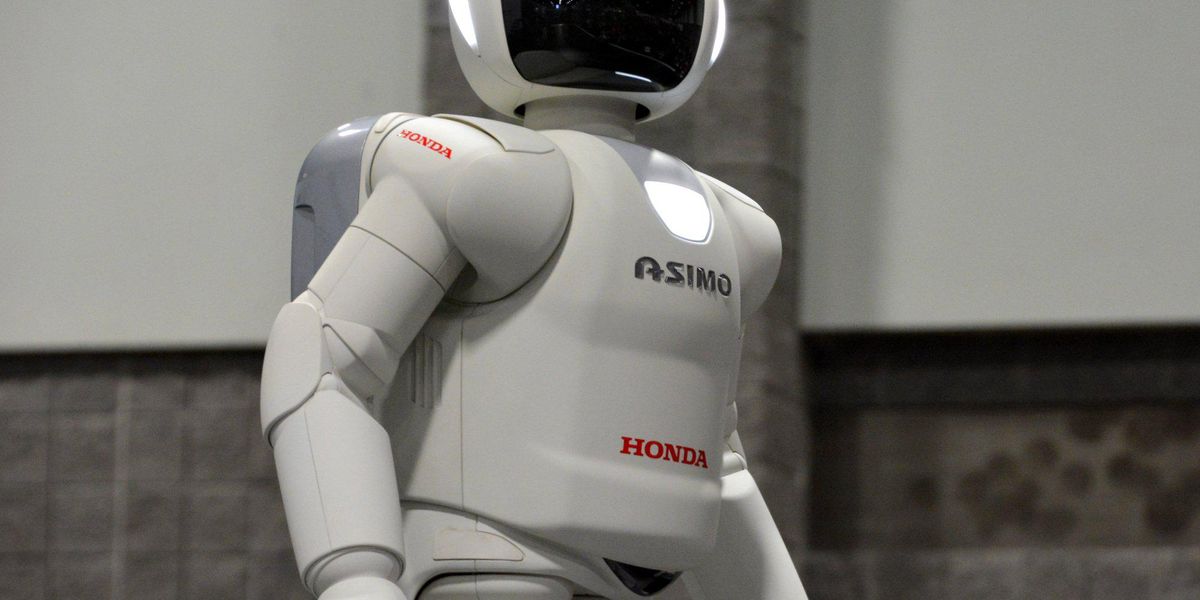
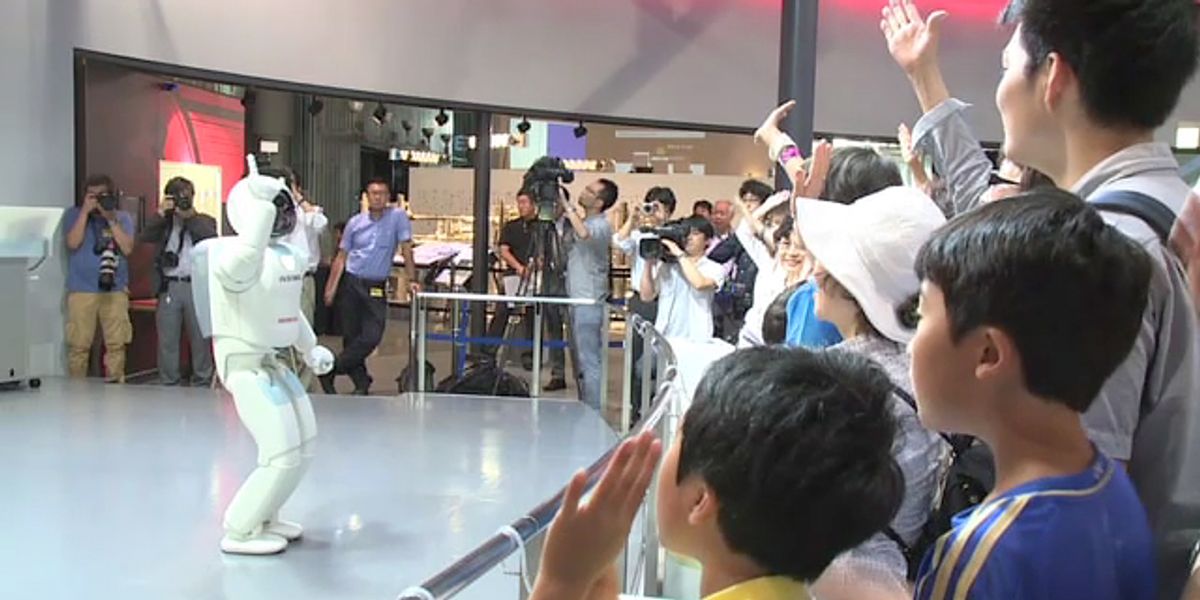
Asimo is a humanoid robot designed to be a helper to people. It can run, dance, hop, and kick a soccer ball. It travels the world as an ambassador to robokind, making humans excited about robotics.
- Creator
- Year
- 2000
- Country
- Japan 🇯🇵
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Asimo stands for Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility, but the acronym was derived from the Japanese word "asi," which loosely translates to "foot" or "leg."


History
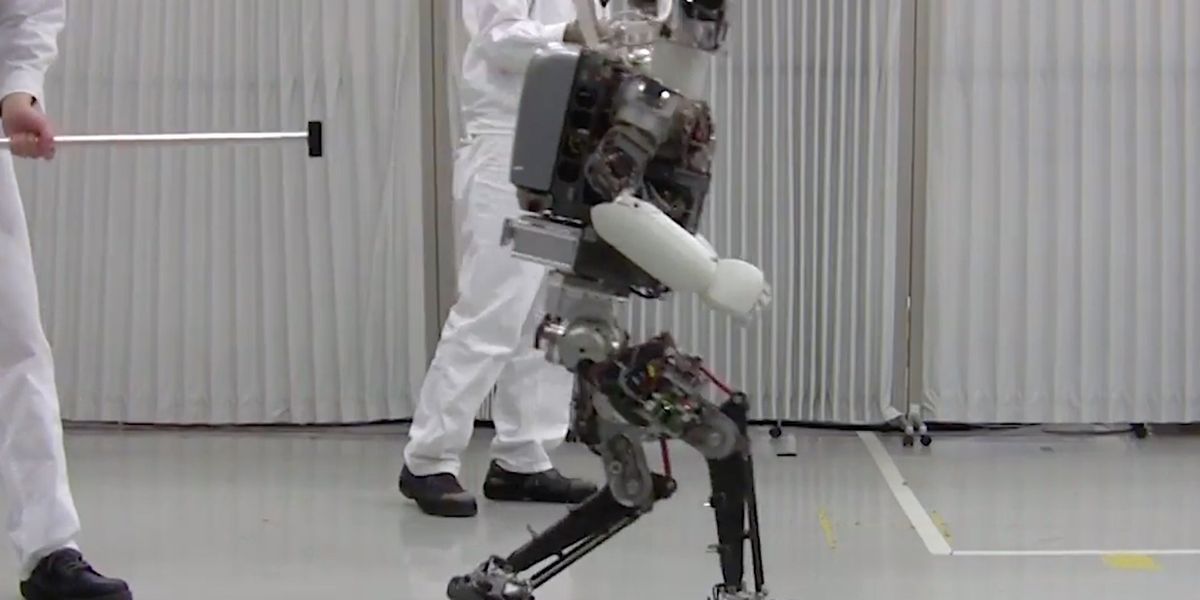
Honda started developing humanoid robots in 1986. Over the next 15 years, the company would build about a dozen prototypes. Early robots (models E1 to E6) focused on legged locomotion. Next, Honda engineers added a head, torso, and arms to the robot to improve balance and add functionality. In 1993, Honda unveiled its first humanoid, the P1, a rather large machine at 1.9 meters and 175 kg. The P1 was followed by the P2 in 1996 and the P3 in 1997. On 31 October 2000, Honda introduced its now-famous humanoid, Asimo. In 2004, Asimo was inducted into Carnegie Mellon's Robot Hall of Fame as the first robot to demonstrate true human-like mobility. A second-generation Asimo debuted in 2005. In November 2011, Honda unveiled an improved design, which it called "all-new Asimo." With enhanced physical capabilities, the new Asimo was capable of running backwards, continuously jumping up and down, and even hopping on one foot. In 2018, however, Honda said it was halting Asimo development in favor of working on robots with more practical applications, like robots for elder care and disaster relief. In early 2022, Honda announced it was retiring Asimo, bringing an end to four decades of impressive advances in robotics that inspired other engineers and captured the public's imagination.


More Images


Specs
- Overview
Able to navigate human environments, recognize faces, and understand speech. Bipedal walking based on ZMP (Zero Moment Point) control approach.
- Status
Discontinued
- Year
2000
- Website
- Width
- 45 cm
- Height
- 130 cm
- Weight
- 48 kg
- Speed
- 9 km/h (running), 2.7 km/h (walking)
- Sensors
Head with cameras and microphones. Torso with gyroscope and accelerometer. Foot with six-axis force sensor. Hands with tactile sensors in the palms and force sensor on each finger.
- Actuators
More than 26 DC motors and brushless DC motors.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 57 (Head: 3 DoF; Arm: 7 DoF x 2; Hand: 13 DoF x 2; Hip: 2 DoF; Leg: 6 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Body made of a magnesium alloy frame covered with a plastic resin.
- Compute
Custom computing and control system.
- Software
VxWorks real-time OS and custom control software.
- Power
51.8-V lithium-ion battery, 1 hour of operation