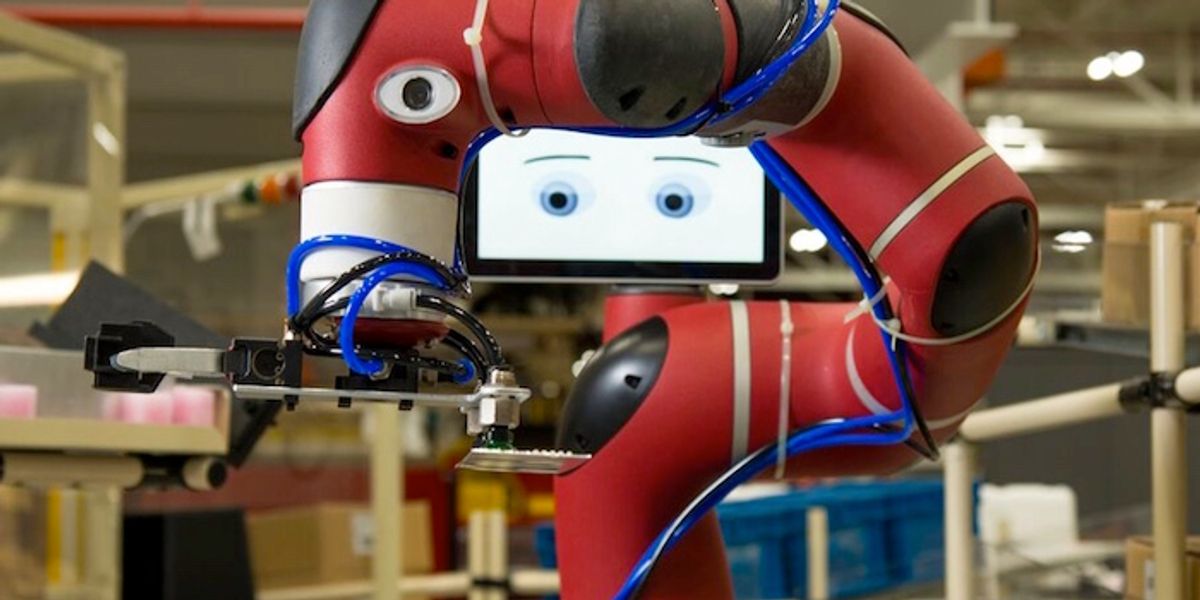
Baxter

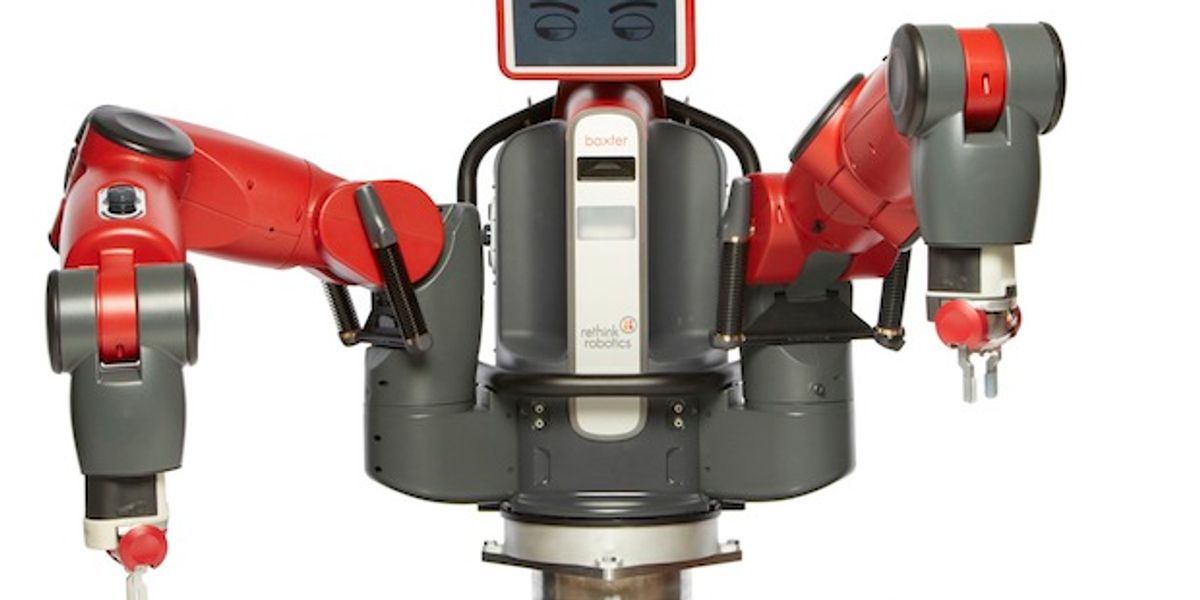
Baxter is a versatile manufacturing robot. Its cameras and force-sensing actuators let it adapt to changes in the environment, and a user can program a new task simply by moving its arms around.
- Creator
(Rethink Robotics shut down in 2018; its patents and trademarks were acquired by Germany's Hahn Group.)
- Year
- 2012
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Baxter doesn't speak, but it nods its LCD head to indicate that it has understood a new command.


History
Rodney Brooks, a cofounder of iRobot and a former director of MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, founded Rethink Robotics, then called Heartland Robotics, in 2008. His goal was to develop an affordable industrial robot that could automate repetitive tasks in small and medium-size manufacturers, working alongside humans and helping them with tasks rather than taking their jobs. The company worked in total secrecy until late 2012, when it changed its name to Rethink Robotics and unveiled its first robot, called Baxter. It introduced a second robot, Sawyer, in 2015. Rethink raised US $62 million in venture funding. The company shut down in 2018.


Specs
- Overview
Equipped with active and passive safety systems and a user-friendly control interface. Able to control movements based on vision and force sensing.
- Status
Discontinued
- Year
2012
- Website
- Width
- 260 cm
- Height
- 94 cm (waist to head)
- Length
- 37 cm
- Weight
- 75 kg (not including pedestal)
- Sensors
Five cameras (one in the head, two in the chest, and one in each forearm). Force sensing based on series elastic actuators. Head with sonar array for detecting humans moving close by.
- Actuators
Series elastic actuators with brushless DC motors, metal and plastic gearboxes, and custom spring element.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 16 (Arm: 7 DoF x 2; Head: 2 DoF)
- Materials
Cast aluminum, thermoplastics, powdered metal parts.
- Compute
Intel-based main computer inside torso. ARM-based motor controller boards inside arms.
- Software
Linux OS and custom control software with ROS (Robot Operating System) integration.
- Power
Standard 110-V power supply
- Cost
- $22,000