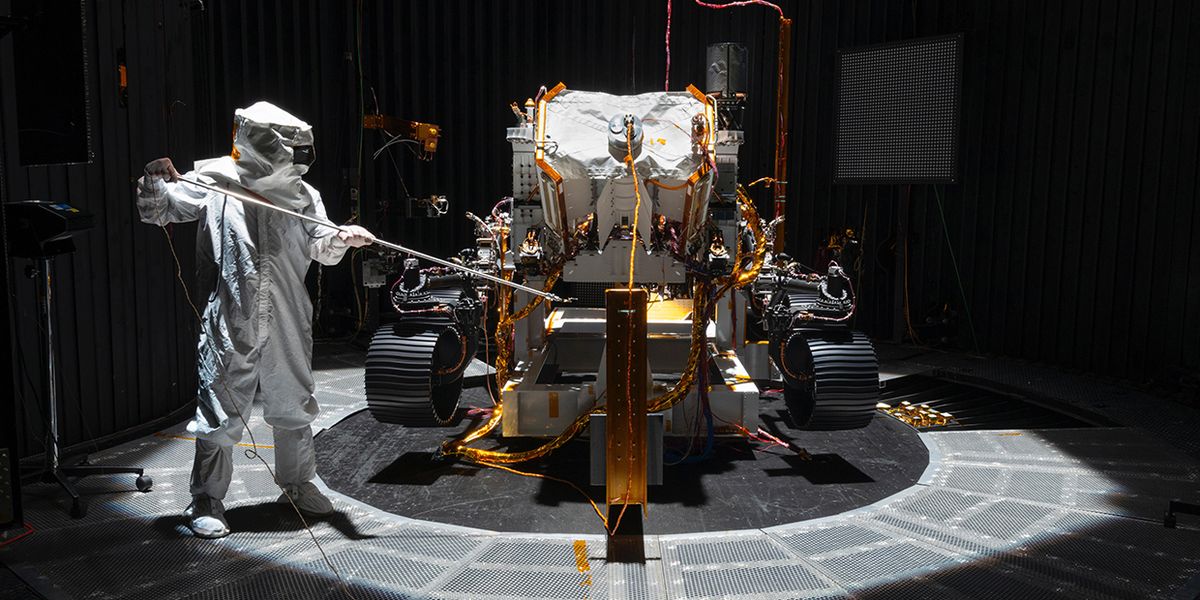
Spirit & Opportunity

Spirit and Opportunity are twin rovers that were sent to explore Mars. They landed in 2004, and their mission was seeking evidence about whether Mars might once have been capable of supporting life.
- Creator
- Year
- 2003
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
Their mission was scheduled to last 90 days, but Spirit survived for six years and Opportunity is still operational.


History
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built the twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity as part of its Mars Exploration Rover mission. Spirit and Opportunity launched on 10 June and 7 July 2003, respectively. Spirit landed on Gusev Crater (a possible former lake) on 4 January 2004; Opportunity landed at the Meridiani Planum (where mineral deposits suggest a wet past) three weeks later. NASA JPL's Pete Theisinger was the Mars Exploration Rover project manager. Steve Squyres of Cornell University, in Ithaca, N.Y., was principal investigator for the Rovers' identical sets of science instruments. Following on the remarkable success of Spirit and Opportunity, NASA JPL developed even bigger and more advanced rovers: Curiosity and Perseverance.


Specs
- Overview
Capable of driving autonomously for short distances. Equipped with rocker-bogie suspension system (for rolling over big rocks).
- Status
Inactive
- Year
2003
- Website
- Width
- 230 cm
- Height
- 150 cm
- Length
- 160 cm
- Weight
- 180 kg
- Speed
- 0.18 km/h (flat, hard terrain)
- Sensors
Two panoramic cameras, two navigational cameras, two front hazard detection cameras, and two rear hazcams. Scientific instruments include: mini-thermal emission spectrometer (for detecting the mineral composition of surface features), microscopic imager (for capturing close-up views of rocks), Mossbauer spectrometer (for detecting iron-bearing minerals), Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (for detecting the elements that make up rocks), and rock abrasion tool (the rover's equivalent of a geologist's rock hammer).
- Actuators
39 Maxon brushed DC motors
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 39
- Materials
Core structure made of composite honeycomb material insulated with aerogel.
- Compute
BAE Systems 20-MHz 32-bit RAD6000 CPU (a radiation-hardened version of the PowerPC); on-board memory includes 128 MB RAM, 256 MB flash, and smaller amounts of other non-volatile memory.
- Software
Custom software
- Power
Solar panels used to recharge two lithium-ion batteries
- Cost
- $820 million (Total cost, including $645 million spacecraft and science instruments, $100 million launch, and $75 million mission and science operations.)