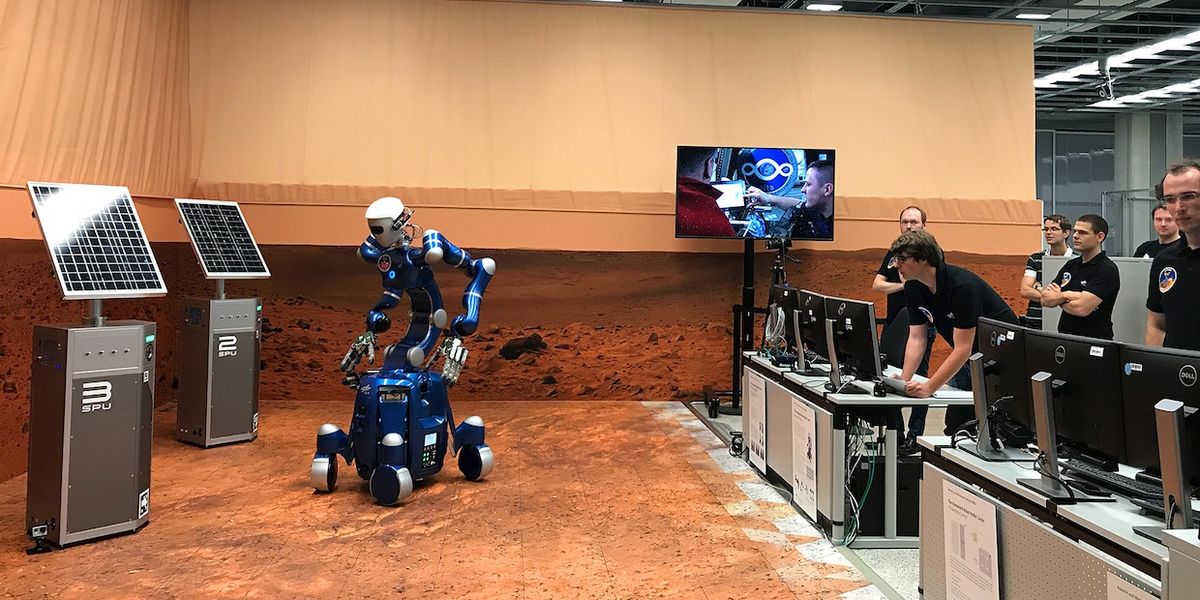
TORO

Toro is an advanced humanoid robot used as a research platform to study bipedal walking and autonomous behaviors combining manipulation and locomotion.
- Creator
- Year
- 2013
- Country
- Germany 🇩🇪
- Categories
- Features
Did you know?
TORO stands for TOrque-controlled RObot. It also means "bull" in Spanish.


Specs
- Overview
Self-contained, with both position and torque control modes. Payload of 10 kg. Based on KUKA-DLR Lightweight Robot (LWR) arm drives.
- Status
Ongoing
- Year
2013
- Website
- Height
- 174 cm
- Weight
- 76 kg
- Speed
- 1.8 km/h (arm speed)
- Sensors
Position and torque sensors in each joint. 6-DoF force/torque sensor in each ankle. Inertial measurement units on torso and head. ASUS Xtion pro in the head. Two FLIR/Point Grey Firefly monochrome cameras in the head. One Intel RealSense SR 300 in the head.
- Actuators
25 motor drive units (based on LWR technology) on arms, legs, and hip. Two Dynamixel servo motors on the neck.
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 39 (Neck: 2 DoF; Arms: 6 DoF x 2; Legs: 6 DoF x 2; Hip: 1 DoF; Hands: 6 DoF x 2)
- Materials
Mostly custom-made parts, milled in aluminum.
- Compute
Two Intel Core i7 computers on torso, one Intel Core i3 computer in the head
- Software
Real-Time Linux based on Kernel 4. Real-time-capable middleware Links and Nodes (developed at DLR). Runtime-configurable hardware abstraction framework Robotkernel (developed at DLR).
- Power
Two 48-V, 6.6-Ah lithium-ion-manganese-oxide battery packs, 1 hour of operation